Teachers' Domain - Digital Media for the Classroom and Professional Development
User: Preview
Source: WISCONLINE
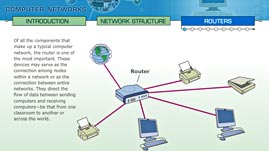
In this interactive activity adapted from the Wisconsin Online Resource Center, discover how computers communicate with one another through networks. Learn about types of networks (local area networks and wide area networks) and three common components: links, nodes, and routers. In addition, investigate some of the advantages and disadvantages of four kinds of network topologies: mesh, bus, star, and ring. Finally, explore the role of routers and how data travels from one network to another.
Computer networks allow computers and other devices to communicate with one another, greatly enhancing their functionality. For example, you are probably familiar with a local area network (LAN), often found in an office or a school computer lab. In this type of network, computers that are connected to one another can exchange files and share software programs and equipment, such as printers and scanners. If the computers were not networked together, each computer would operate independently. You would only be able to access the printer from the computer it was connected to, and you would have to physically transfer files from one computer to another using a disk or flash drive. By creating a network with cables, wires, or wireless connections, the computers and devices can easily share information.
On a much larger scale, the Internet connects computers all over the world. This global network consists of millions of computers, including private, academic, business, and governmental machines, which are all linked together. This puts a wealth of information at users’ fingertips, and with it the capacity to interact and share data worldwide. Without this computer network, you could not surf the Web or even send an email!
In industry, the ability to exchange information through computer networks is extremely useful. For example, imagine a company that manufactures and sells steel-frame bicycles. This company would greatly benefit from a convenient means of communication among its different departments, such as sales, engineering, production, purchasing, billing, and shipping. Computer networks and specialized software can streamline the process. When an order is placed for bicycles, someone in the sales department enters the order into a computer, which then provides the information to other departments that can initiate production if the bicycles are out of stock. If there is not enough material in stock, purchasing can order more steel. The production team uses production specifications placed online by engineering and design to set up the manufacturing equipment, and the shipping department receives production data to schedule transport. When the products ultimately ship to the customer, the billing department sends out an invoice, or bill.
Automated manufacturing systems also make use of computer networks by sharing data among different parts of the system. For example, diagnostic information can be obtained from a remote location to troubleshoot problems, devices can be programmed from a remote location, and a computer in one part of the system that detects a problem can even communicate to other computers controlling different sections of the machinery to shut them down. Networked machines enable the system to run more efficiently than would otherwise be possible.
 Loading Standards
Loading Standards Teachers' Domain is proud to be a Pathways portal to the National Science Digital Library.
Teachers' Domain is proud to be a Pathways portal to the National Science Digital Library.
